Product Overview
Product Overview
What Is NAD+
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a critical coenzyme found in all living cells, playing a central role in cellular metabolism, energy production, and signaling. As the oxidized form of NADH, NAD+ is essential for transferring electrons in biochemical reactions and supporting a variety of biological processes including DNA repair, immune response, circadian rhythm regulation, and enzyme activity. NAD+ levels naturally decline with age, contributing to many age-related conditions and decreased cellular efficiency. Research into supplementation has demonstrated that restoring NAD+ levels can help counteract some of these declines, making it an exciting area of study for longevity and regenerative medicine.
NAD+ Structure
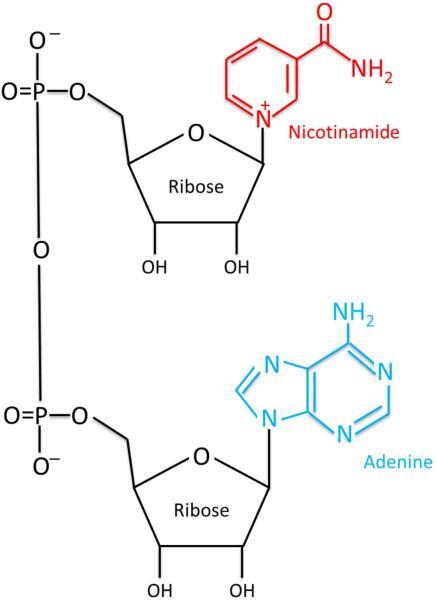
Molecular Formula: C21H27N7O14P2
Molecular Weight: 663.43 g/mol
CAS Number: 53-84-9
Synonyms: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, beta-NAD, NAD, Endopride
NAD+ Effects and Research
NAD+ has been shown to support a wide range of cellular functions. By activating enzymes like sirtuins and PARPs, NAD+ helps regulate gene expression, repair DNA damage, reduce inflammation, and maintain healthy mitochondrial function. Studies have demonstrated benefits in preserving neuronal health, improving vascular integrity, increasing muscle strength, and even reversing certain signs of aging in animal models. Additionally, NAD+ shows synergistic effects when combined with CoQ10, resveratrol, B vitamins, and alpha-lipoic acid — further supporting cellular resilience and longevity. Research suggests that NAD+ also plays a role in neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular health, metabolic disorders, and recovery from addiction by modulating stress and reward pathways.
NAD+ in Aging and Beyond
Recent findings highlight NAD+ as a key molecule in the fight against age-related decline. Mitochondrial dysfunction and reduced cellular repair mechanisms are hallmarks of aging that NAD+ can help mitigate. Supplementation has been shown to improve muscle function, cognitive performance, and overall vitality in preclinical studies. Researchers are also exploring its role in combating neurodegeneration, inflammation, and metabolic diseases like type 2 diabetes.
Referenced Citations
- Elysium Health, “NAD+ Science 101.”
- Healthline, “Nicotinamide Riboside: Benefits, Side Effects and Dosage.”
- Matthews et al., “Coenzyme Q10 administration and neuroprotection.”
- WebMD, “What You Need to Know About Resveratrol Supplements.”
- Sun et al., “The Mitochondrial Basis of Aging.”
- Stipp, “Beyond Resveratrol: The Anti-Aging NAD Fad.”
- Gomes et al., “Declining NAD+ and pseudohypoxia.”
- Imai & Guarente, “NAD+ and sirtuins in aging and disease.”
- Mendelsohn & Larrick, “Reversal of skeletal muscle aging.”
- Kang et al., “Exercise training and mitochondrial dysfunction.”
- Ringholm et al., “Resveratrol supplementation and exercise training.”
- Lloret & Beal, “PGC-1α, Sirtuins and PARPs in Huntington’s Disease.”
- Shan et al., “NAD+ and Parkinson’s Disease.”
- Maddison & Giorgini, “The kynurenine pathway in neurodegeneration.”
- Garten et al., “NAMPT and NAD metabolism.”
- Yamaguchi & Yoshino, “Adipose Tissue NAD+ Biology.”
- Humiston, “Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide.”
Disclaimer
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
The products offered on this website are furnished for in-vitro studies only. In-vitro studies (Latin: in glass) are performed outside of the body. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat or cure any medical condition, ailment or disease. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law.
Storage Instructions
All of our products are manufactured using the Lyophilization (Freeze Drying) process, which ensures that our products remain 100% stable for shipping for up to 3-4 months. Once the peptides are reconstituted (mixed with bacteriostatic water), they must be stored in the fridge to maintain stability. After reconstitution, the peptides will remain stable for up to 30 days.
Lyophilization is a unique dehydration process, also known as cryodesiccation, where the peptides are frozen and then subjected to low pressure. This causes the water in the peptide vial to sublimate directly from solid to gas, leaving behind a stable, crystalline white structure known as lyophilized peptide. The puffy white powder can be stored at room temperature until you're ready to reconstitute it with bacteriostatic water.
Once peptides have been received, it is imperative that they are kept cold and away from light. If the peptides will be used immediately, or in the next several days, weeks or months, short-term refrigeration under 4°C (39°F) is generally acceptable. Lyophilized peptides are usually stable at room temperatures for several weeks or more, so if they will be utilized within weeks or months such storage is typically adequate.
However, for longer-term storage (several months to years) it is more preferable to store peptides in a freezer at -80°C (-112°F). When storing peptides for months or even years, freezing is optimal in order to preserve the peptide’s stability.
For further information on proper storage techniques, click the link below:






